|
Getting your Trinity Audio player ready...
|
Organizations rely on a process called “vulnerability management” to help identify, analyze, treat and report on security vulnerabilities within their systems and applications. This process, when combined with other cornerstone strategies and techniques, helps set the foundation for a strong security posture through threat prioritization and attack surface reduction.
Vulnerability Management Organizations rely on a process called “vulnerability management” to help identify, analyze, treat and report on security vulnerabilities within their systems and applications. This process, when combined with other cornerstone strategies and techniques, helps set the foundation for a strong security posture through threat prioritization and attack surface reduction.
Today’s security environments are under constant pressure from sophisticated attackers and ever-growing complexity. The process of vulnerability management is key to addressing these risks, as it provides a clear window into the current state of organizational security. Vulnerability risk management should be undertaken continuously, however, as changes to internal systems (and evolving external threats) are always creating new security gaps.
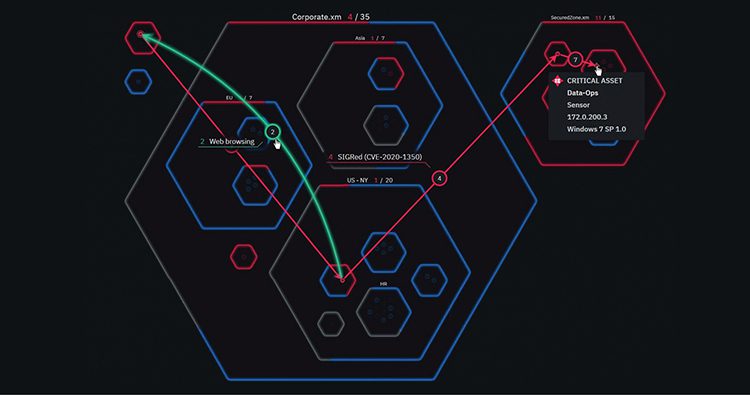
Organizations often use tools called vulnerability scanners to identify problems within their systems and software. These tools produce a vulnerability scan report, which identifies existing issues within the environment. Once these problems are identified in the scan, they must be contextualized in order to determine how to best mitigate the issue.
Vulnerability assessments are performed within the larger framework of vulnerability management. These assessments can help organizations take snapshots of their relative strengths and weaknesses and serve as accumulated intelligence for the crafting of an overarching vulnerability management action plan.
- The Four Components of Vulnerability Management
- Cyber vulnerability management is generally comprised of four individual components:
- Identification of vulnerabilities
- Analysis of vulnerabilities
- Treatment of vulnerabilities
- Reporting of vulnerabilities
When identifying vulnerabilities, organizations may begin by scanning network systems, identifying open ports/services, remotely logging in to acquire system data and correlating that information with known vulnerabilities. This means vulnerability scanners will pinpoint computing devices, servers, firewalls etc., then probe for various attributes (configurations, user accounts etc.), before associating what it discovers with vulnerabilities from a public database.
This process has been known to cause issues if the scans are not properly configured, however. Should this occur, the scan may cause problems within the system it is evaluating. Additionally, vulnerability scanners can sometimes create false positives.
Once vulnerabilities are identified, they must be evaluated for risk. Most vulnerability management solutions will score these risks (by using the Common Vulnerability Scoring System or some other set of metrics), providing organizations with guidance on risk prioritization.
The next step is treatment, which may include remediation (a full fix or patch), mitigation (reducing the likelihood of a vulnerability being leveraged) or acceptance (if the vulnerability poses limited risk or if the cost of the fix outweighs the possible damage). While today’s vulnerability management software typically provides prioritized treatment recommendations, it may be necessary to examine this step in closer detail with all key stakeholders, especially if the remediation is significant or wide-ranging.
Finally, reporting data allows organizations to analyze the results of prior scans, tests or assessments. Most vulnerability management software products have dashboards that make this information easily accessible. When gathered and contextualized, it can play an important role in helping defenders optimize their tactics and overall vulnerability management strategy.
Vulnerability Management vs Penetration Testing
As mentioned above, vulnerability scans come with some limitations, especially with regard to false positives or system disruptions. Penetration testing can be incorporated into the vulnerability management process to help provide a clearer picture of the true state of a security environment. Not only can penetration tests help resolve false positives, they can also uncover vulnerabilities that are entirely overlooked by a conventional scan. When performed in an automated and continuous fashion, penetration tests provide a deep level of risk assessment that can help organizations deal with evolving threats and system changes.
In Conclusion
Vulnerability management can play a key role in helping organizations identify, evaluate and treat threats, while providing critical reporting data for the optimization of future strategies.