|
Getting your Trinity Audio player ready...
|
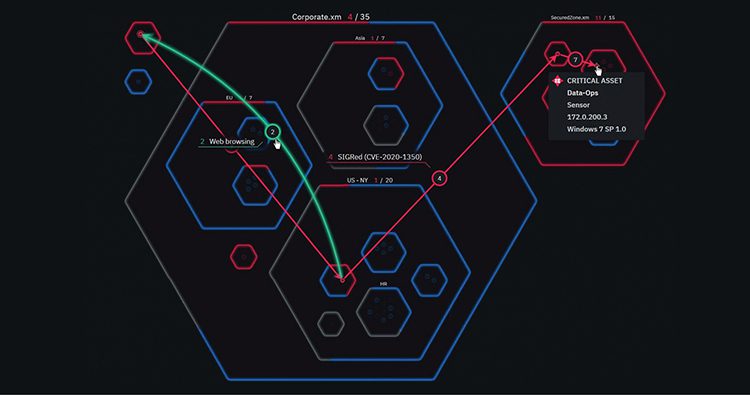
Having a strong security posture is a core objective for modern organizations. Yet measuring the strength of these postures is often challenging, given their breadth and complexity. A cyber risk score provides an objective framework for the evaluation of a security posture. By converting these evaluations into an easy-to-grasp representation of qualitative cyber risk scoring, organizations can better understand how safe their assets are and where they need to improve.
The concept of a cybersecurity posture helps enterprises view their information security efforts holistically. An IT security posture encompasses all security strategies, policies, programs and solutions that an organization has in place. The end goal is to develop a posture that is strong and resilient, and maintain that posture in the face of evolving threats and risks.
Achieving that goal requires a useful tool or framework for measuring the strength of such postures. A cyber risk score calculation is one of the most popular and effective methods for making such measurements.
How Cyber Security Risk Assessment Scoring Methodologies Work
Much like FICO or credit scores, a risk score for cybersecurity provides an easy to grasp representation of the strength of a security posture. Higher ratings mean stronger defenses. While credit scores provide third parties insight into whether another party is financially responsible, cyber risk scores provide insight into whether enterprises are doing enough to protect against data breaches.
The scoring process does not include conventional risk assessment activities such as pen testing on onsite visits. There is also no single universal methodology for cybersecurity posture scoring. Different score providers use different metrics to arrive at their conclusions. In broad strokes, however, scores are generated from data and inputs gathered from the organization being scored. These inputs may be gathered manually or dynamically by the provider or supplied by the enterprise being scored.
The types of inputs gathered may be external or internal and often include elements such as:
- The number of employees
- The type of security technologies used by the enterprise
- The type of security processes in place
- Evaluation of IP addresses and traffic
- Chatter on the dark web or in hacker circles that targets or refers to the enterprise being scored
The Benefits of Scoring for Cyber Risk
Organizations that score well have objective validation that they are taking the right steps to protect their data. This provides potential and current customers and partners with independent proof that an enterprise is meeting its cybersecurity obligations. This, in turn, can ultimately increase revenue and profitability. Security is increasingly seen as a competitive differentiator, just like product or service quality and price. Scoring by neutral parties has become essential to this process.
A report from Gartner reinforced the value of IT security scoring. In that report, Gartner said “cybersecurity ratings will become as important as credit ratings when assessing the risk of existing and new business relationships…these services will become a precondition for business relationships and part of the standard of due care for providers and procurers of services. Additionally, the services will have expanded their scope to assess other areas, such as cyber insurance, due diligence for M&A and even as a raw metric for internal security programs.
Ultimately, today’s organizations are becoming more reliant on risk scoring to not only provide an objective benchmark of the progress they are making, but also for vendor risk management purposes and validation of their efforts in the eyes of clients and partners.
Scoring well requires a commitment to continuous cybersecurity posture improvements and smart cyber risk prioritization. Both of these should be cornerstone objectives for any enterprise seeking to keep their assets safe and their scores consistently high.