|
Getting your Trinity Audio player ready...
|
Risk exposure is a quantification of the vulnerability of an individual, organization, or asset to adverse events or uncertainty. It can show how susceptible an entity may be to financial, operational, or reputational losses as a result of security breaches, market fluctuations, natural disasters, technological failures, legal liabilities and more. The extent of exposure to risk depends on numerous factors: what the entity does, where it is geographically located, what industry it operates in, its financial structure, and the risk management strategies it has in place.
How do we assess risk exposure? The risk exposure assessment process identifies and evaluates potential threats, estimates their potential severity, and determines the adequacy of existing safeguards. This process helps decision makers prioritize resources, implement risk reduction strategies, and develop contingency plans. Yet it requires in-depth insights that are only achieved through continuous monitoring and adjustment of risk management strategies in response to change.
Types of risk exposure
There are multiple types of risk that individuals, businesses, and organizations may be exposed to. Each type requires unique assessment, management, and mitigation strategies to minimize negative impacts. Some of the most common include:
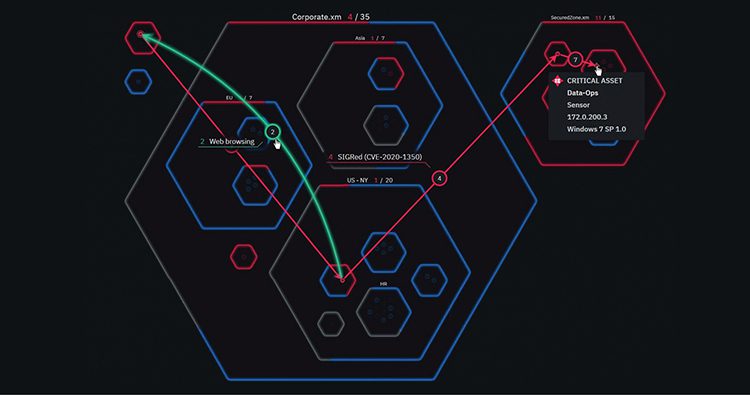
- Cybersecurity risk – Threats to digital systems, data breaches, and unauthorized access (more on this below)
- Operational risk – Risk arising from errors, fraud, system failures, and disruptions to business operations owing to systems, people, or external events
- Market risk – Potential losses resulting from fluctuations in interest rates, foreign exchange rates, stock prices, or other market conditions
- Political/geopolitical risk – Risk from changes in political landscapes, policies, or international relations
- Reputational risk – Potential harm from negative public perception about an organization’s brand, trustworthiness, and success
- Legal/regulatory risk – Non-compliance with laws, regulations, or industry standards, which can lead to legal actions or fines
- Environmental risk – Risk resulting from climate change, natural disasters, and ecological concerns
What is risk exposure in the context of cybersecurity?
In the context of cybersecurity, risk exposure means the vulnerability of an organization to cyberthreats and cyberattacks, which might compromise the confidentiality and integrity of sensitive information, or the availability of digital assets. This risk may arise from a range of factors, including:
- Cyber hygiene – The efficacy of cybersecurity practices like patch management, incident response, access control, encryption and more
- Data sensitivity – The sensitivity of the organization’s data, whether it is personal and financial information or intellectual property or trade secrets
- Threat landscape – The dynamic cyberthreat landscape, including existing and emerging attack vectors, social engineering techniques, malware, ransomware, and more
- Vulnerabilities – Vulnerabilities in software, hardware, networks, and processes that can be exploited by threat actors
- Regulations – Compliance with cybersecurity regulations and industry standards
- Third-party risk – Potential exposure from cybersecurity of third-party vendors and partners
All these types of cyber risks and more need to be mitigated with robust cybersecurity measures, regular vulnerability assessments, incident response plans, ongoing employee education about security best practices, and updated threat intelligence. Effective cyber risk exposure management reduces the possible impact of cyber incidents – protecting digital assets, reputation, and business continuity.
How do you calculate risk exposure?
To calculate risk exposure, organizations conduct a systematic assessment of potential threats and their impacts, which generally involves the following steps:
- Identify and categorize relevant risks, taking into consideration factors such as market conditions, operational processes, legal requirements, and technological vulnerabilities
- Assess the likelihood of each risk identified occurring and estimate the potential magnitude of its impact
- Quantify the likelihood and impact of each risk, calculating a risk exposure score
- Prioritize various risks based on exposure scores, focusing resources on high-exposure areas
- Mitigate and manage identified risks via risk mitigation strategies such as risk avoidance, risk transfer, risk reduction or risk acceptance
- Monitor and continuously review the effectiveness of risk management strategies – adjusting as necessary based on emerging risks or evolving circumstances
Calculating a risk exposure formula for effective risk management empowers stakeholders to understand the potential impact of various threats and make informed decisions to protect assets and enhance resilience.
Benefits of understanding risk exposure
Risk exposure is a compass guiding organizational stakeholders through a complex and uncertain landscape. It quantifies the vulnerability of entities to a range of financial, operational, and reputational adversities. It helps decision makers decipher potential hazards, fortify defenses, and craft contingency blueprints.
Managing exposed risk offers numerous benefits. By minimizing the potential impact of threats and safeguarding critical assets, risk exposure management enhances resilience and ensures business continuity. It enables more informed decision-making and helps optimize resource allocation. It fosters a proactive and adaptive organizational culture – raising employee awareness and engagement. It protects against financial loss, safeguards investments, improves creditworthiness, and enhances stakeholder trust. Most importantly, proactive risk management enables organizations to survive and thrive in today’s highly competitive market space – navigating uncertainties while still pursuing growth and innovation.