Cloud platforms such as Amazon Web Services (AWS) have transformed how we do business. They allow organizations access to highly scalable and flexible computing architecture for a fraction of the cost of a fully in-house solution.
However, as organizations migrate to the cloud with record speed, security sometimes falls by the wayside. The complexity of managing complex hybrid and multi-cloud environments can create difficult new cybersecurity challenges. In the worst cases, it can lead to devastating data breaches with serious financial and reputational costs attached.
Fortunately, getting ahead of the curve by taking some smart steps to address these risks right now can help greatly lower the odds of a successful attack.
With that in mind, let’s review some key AWS security recommendations that will help you safeguard your business-critical assets.
AWS Cloud Security Best Practices
Your AWS cloud security strategy should be built on a foundation of careful consideration. To help you lay that foundation, here are some of the most impactful AWS security architecture best practices and AWS security recommendations you can incorporate right now:
- Understand Amazon’s “shared responsibility” approach to security. Amazon takes responsibility for the security of its infrastructure and will notify you if a problem occurs. However, AWS users are responsible for the secure configuration of their AWS environments, the use and management of data and compliance/governance. In other words, don’t expect AWS to be the last or even first line of defense.
- Don’t adhere to the standard checklist-based compliance approach. Why? Because it does not work in a dynamic cloud environment where configurations and account settings change constantly. The compliance process requires automation and continuous insight into changes to controls, configurations and settings.
- Pinpoint your security requirements. Why is it important to define and categorize assets in AWS? Because you cannot protect what you don’t see or understand. Identify these assets and group them accordingly. After they have been identified, all assets should be assigned a security classification based on risk, criticality, etc. These classifications then serve as the baseline for determining what level of protection must be deployed.
- Next, ensure you are using security tools that are specifically designed to meet the challenges of operating in the cloud. If your solution is designed for the cloud, they will work optimally within their deployment environment.
- Take a layered approach and enable encryption. One firewall isn’t enough; install virtual firewalls on all virtual networks to effectively control traffic and reduce risk. Enabling encryption on AWS is simple, so there is no reason not to do so.
- Accessibility is a cloud selling point, but it can also be a security weakness. Cloud resources can be accessed without going through existing perimeters and the security measures that are in place in those environments. The solution is simple: Manage cloud access more effectively. Make sure only people who truly need access have that permission.
- Identity and Access Management — based around the principle of AWS least privilege — can help you apply proper permissions at a granular level. Use this tool to create policies that ensure that permissions and privileges are properly granted. Instead of basing policies around individual users, connect them to roles. This will reduce the odds of the wrong person gaining or retaining the wrong set of permissions or privileges.
- Segment and separate workloads. This makes it harder for a successful breach to occur and will help contain the damage if the worst does happen, as you will make it more difficult for an attacker to move freely and target and steal critical assets.
How the Right Software Tool Can Support AWS Security Best Practices
As mentioned above, it is critically important to incorporate cloud-specific security tools to help you hold up your end of the AWS shared responsibility model.
The key challenge with AWS cloud security is complexity. These dynamic cloud environments are in a state of constant change and attack surfaces are constantly growing. This means that new vulnerabilities are perpetually arising.
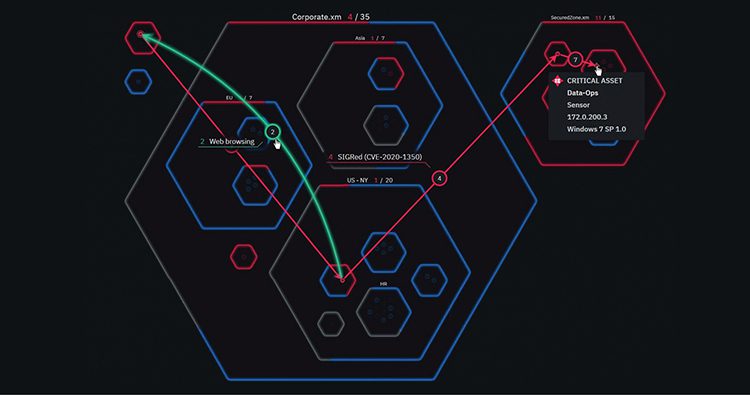
To manage these risks, it is imperative to have a tool that allows for a continuous view of the attack surface. XM Cyber provides that critical “attacker perspective” by providing continuous visibility into the vulnerabilities created by the dynamism of cloud environments. We show you where you are vulnerable and how those vulnerabilities can be exploited to jeopardize your most critical assets.
This provides a true picture of risk on an ongoing basis — and allows your team to focus on the small number of exposures that represent a real danger.
Shahar Solomon is Customer Operations Team Leader at XM Cyber
Related Topics